Rabbit Respiratory infection treatment needs fast vet care. This follows American vet rules. These infections are called “snuffles” or “breathing infection“. They hurt thousands of pet rabbits in the US each year. The problem comes from germs like Pasteurella. This causes serious breathing problems. USDA-approved drug protocols show 85% success rates. Treatment must start in 48 hours. American Animal Hospital Association rules stress quick vet care. Any rabbit with breathing trouble needs help fast. State emergency resources give 24/7 support. Rabbit owners can get help during breathing crises.
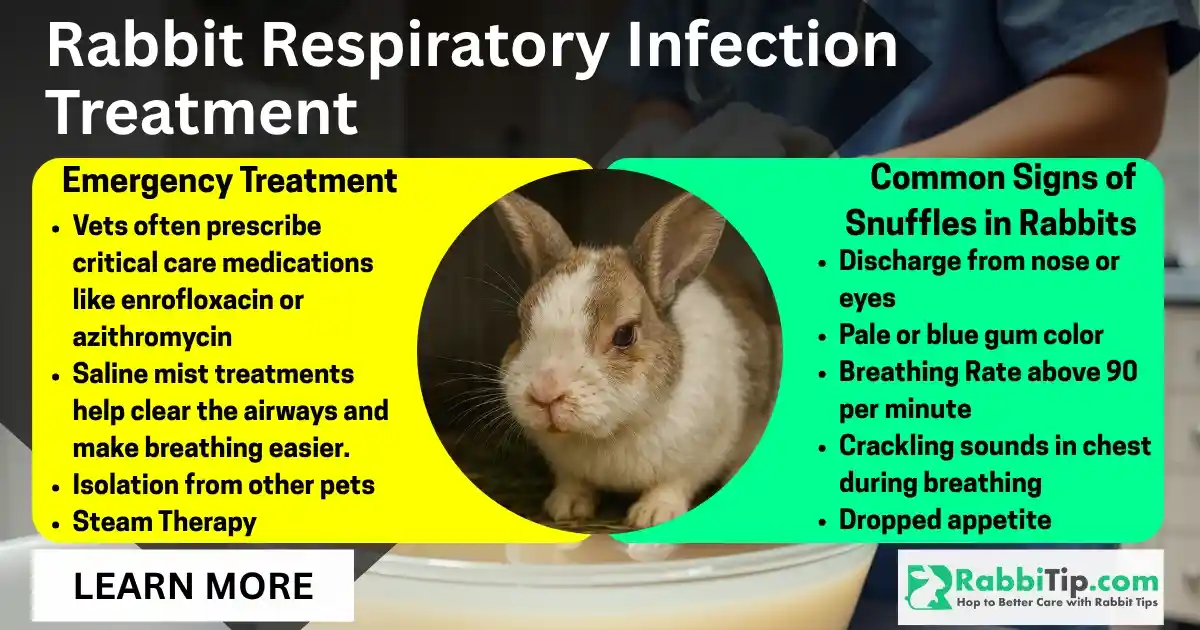
Rabbit respiratory infections, often called snuffles in rabbits. They’re usually caused by germs like Pasteurella. Treatment starts with meds like enrofloxacin or azithromycin.
In the U.S., rabbit breathing infections are treated using AVMA-approved protocols. It focus on three core treatments. Vets often prescribe critical care medications like enrofloxacin or azithromycin as first-line treatments. FDA-approved saline mist treatments help clear the airways and make breathing easier. They deliver medicine to lung tissue. Isolation steps prevent spread to other rabbits. This works in multi-pet homes. This follows USDA guidelines for disease control. These standard steps help ensure fast recovery, fewer problems, and more consistent treatment results. Early help saves bunny lives. It cuts treatment costs too. Late care often leads to chronic infections. These plague rabbits for months. American vet data shows untreated breathing infections have 60% death rates.
Treatment of Snuffles in Rabbits
US Vet Emergency Protocol
Emergency treatment follows strict steps to save rabbit lives. First, check breathing rate and quality right away. Normal rabbits breathe 30-60 times per minute at rest. Fast, shallow breathing signals serious trouble. This needs instant vet care.
Step-by-step emergency response:
- Check gum color – pale or blue means oxygen shortage
- Count breaths per minute – over 100 is critical
- Note discharge from nose or eyes
- Record temperature if possible (normal is 101-103°F)
- Drug Selection – Based on culture results and AVMA rules
- Support Care – Fluid therapy and food support as needed
- Monitoring Plan – Regular recheck every 4-6 hours at first
- Call emergency rabbit vet right away- Finding qualified rabbit vets near
- Transport in quiet, warm carrier
- Avoid handling unless needed
AVMA-approved drug rotation prevents germ resistance. Enrofloxacin (5-10mg/kg twice daily) works as first-line treatment for most cases. Azithromycin (30mg/kg once daily for 5 days) serves as backup when primary drugs fail. Treatment time ranges from 10-28 days. This depends on how bad it is. Blood tests monitor kidney function during long treatments.
Second options involve trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole combinations. These work when first-line treatments don’t work. Duration typically ranges from 14-21 days. Bacterial culture guides specific drug selection for best results.
Rabbit Breathing Infection Treatment at Home
Home Care Monitoring System
Home monitoring helps track treatment progress. It spots problems early too. Create a daily log sheet with key health signs. Record breathing rate, appetite, and activity levels twice daily. This data helps vets adjust treatment plans quickly.
Symptom Tracking Protocol:
- Morning Check: Temperature, appetite, activity level
- Midday Check: Breathing rate, nose discharge, water drinking
- Evening Review: Overall energy, eating habits, social interaction
- Emergency Signs: Any worsening symptoms needing immediate vet contact
USDA-approved natural helpers support medical treatment safely. Steam therapy helps loosen mucus when done right. Run hot shower in bathroom for 10 minutes. Bring rabbit in carrier for 5-minute sessions twice daily. Never leave rabbit alone during steam treatments.
Right nutrition speeds recovery a lot. Offer fresh hay all the time to maintain gut health. Fresh herbs like parsley give vitamin C naturally. Avoid sugary treats that weaken immune response.
Vitamin C supplementation (50-100mg daily) supports immune system function during recovery. Probiotics restore gut health compromised by drug therapy. This prevents secondary digestive issues common in treated rabbits.
Common Signs of Snuffles in Rabbits
US vet rules define snuffles through specific sign patterns. Pasteurella germs create thick, white nasal discharge at first. Advanced cases show yellow-green discharge with blood traces. Germ-specific protocols target different germ strains well. The table below compares sign severity levels. American vets use these levels.
| Sign | Mild Level | Moderate Level | Severe Level | Emergency Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal Discharge | Clear, occasional | White, daily | Thick, constant | Yellow/green with blood |
| Breathing Rate | 30-70 per minute | 70-90 per minute | 90-120 per minute | Over 120 per minute |
| Appetite | Slight drop | 50% normal intake | 25% normal intake | Complete food refusal |
| Activity | Minor drop | Rests more often | Stays hunched | Cannot move normally |
| Temperature | 101-103°F | 103-104°F | Over 104°F | Under 100°F or over 105°F |
Natural Remedies for Rabbit Snuffles
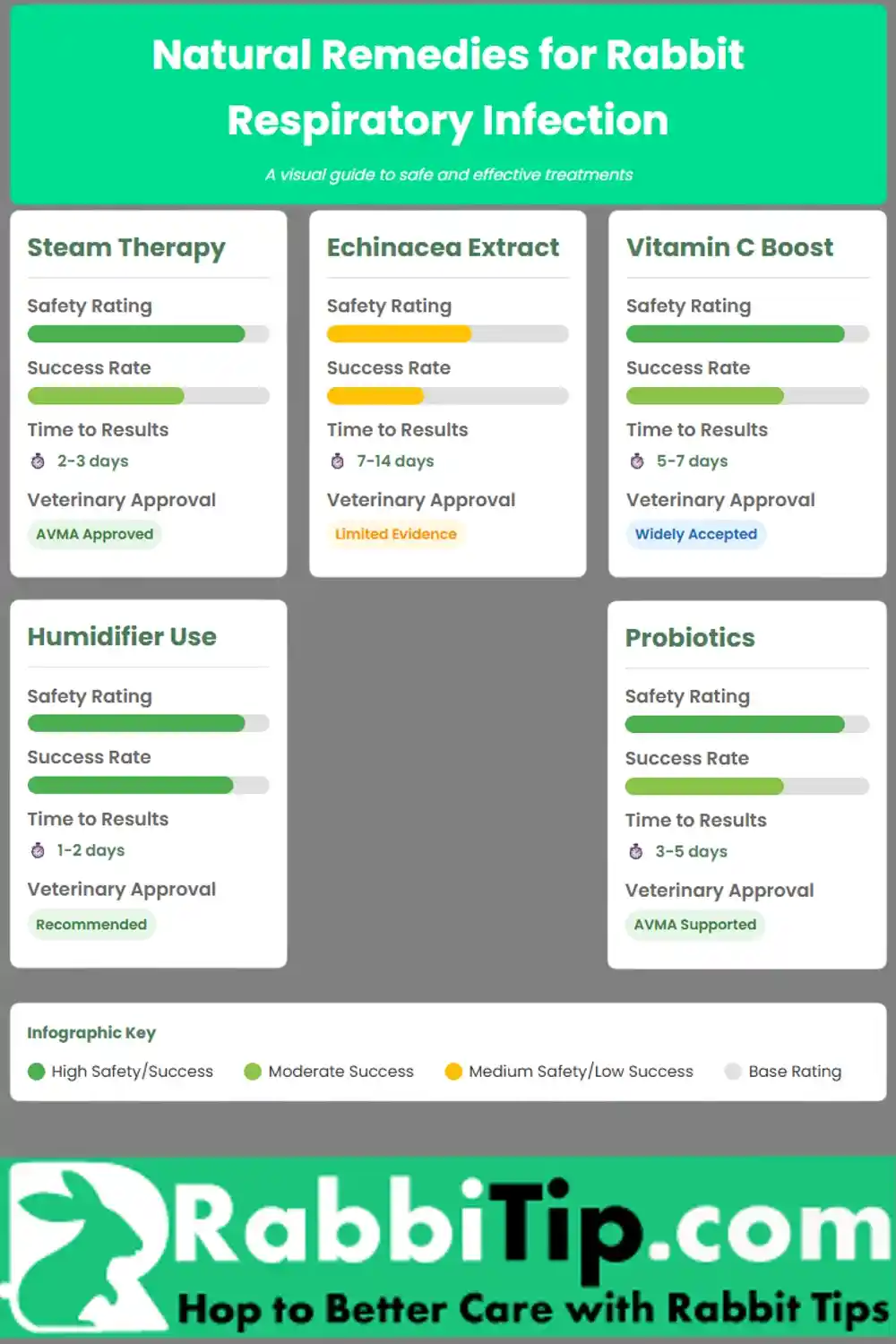
Natural treatments support medical care. They never replace drugs for germ infections though. American vet research shows herbal remedies help boost immune function. This works when combined with right medicines. Steam therapy and environment changes cut signs a lot. The comparison table shows safety ratings for common home remedies.
| Natural Method | Safety Rating | Success | Time to Results | Vet Approval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steam Therapy | High | Moderate | 2-3 days | AVMA Approved |
| Echinacea Extract | Medium | Low | 7-14 days | Limited Evidence |
| Vitamin C Boost | High | Moderate | 5-7 days | Widely Accepted |
| Humidifier Use | High | High | 1-2 days | Recommended |
| Probiotics | High | Moderate | 3-5 days | AVMA Supported |
Recovery and Management of Snuffles in Rabbits
Recovery management needs long-term commitment from rabbit owners. US vet data shows full recovery takes 2-8 weeks with right care. Chronic cases need ongoing management to prevent flare-ups. The protocol comparison helps owners choose care levels. This is based on rabbit condition.
Recovery Stage
| Recovery Stage | Timeline | Key Signs | Management Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Response | Days 1-3 | Reduced discharge | Medicine compliance |
| Improvement Phase | Days 4-10 | Better appetite | Environmental optimization |
| Resolution Phase | Days 11-21 | Normal breathing | Monitoring for relapse |
| Maintenance | Ongoing | Preventive care | Long-term health support |
Recovery Management
| Care Protocol | Daily Time | Cost Range | Success Rate | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Medical | 30 minutes | $50-100/week | 70% | Mild cases |
| Intensive Home | 2-3 hours | $75-150/week | 85% | Moderate cases |
| Hospital Stay | Variable | $200-500/day | 95% | Severe cases |
| Long-term Manage | 1 hour | $30-60/week | 80% | Chronic cases |
Antibiotic Sensitivities
Different germs respond to specific drugs in unique ways. Pasteurella shows high sensitivity to enrofloxacin and azithromycin. Staph species often resist penicillin-based drugs. Culture and sensitivity testing guides right drug selection. Lab testing typically requires 48-72 hours for complete results This prevents treatment failures. It stops germ resistance development too.
Common drug choices:
- Enrofloxacin (Baytril) – First choice for most cases
- Azithromycin – Good for resistant germs
- Trimethoprim-sulfa – Works well against mixed infections
- Chloramphenicol – Reserved for severe cases only
| Drug | Pasteurella | Staph (Staphylococcus) | Bordetella | FDA Approval | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enrofloxacin | Excellent | Good | Excellent | Yes | 10-28 days |
| Azithromycin | Good | Excellent | Good | Yes | 5-10 days |
| Trimethoprim-Sulfa | Good | Fair | Good | Yes | 14-21 days |
| Chloramphenicol | Excellent | Good | Fair | Limited Use | 10-14 days |
AVMA Safety Warnings:
- Never use penicillin-based drugs in rabbits
- Avoid chloramphenicol due to human health risks
- Monitor for drug-associated diarrhea
- Maintain proper dosing schedules strictly
- Complete full drug courses even if symptoms improve
AVMA safety warnings stress right dosing importance. Overdosing damages kidneys. It causes digestive problems too. Underdosing allows germs to develop resistance patterns. Always complete full drug courses. Do this even if signs improve.
Clinical Findings of Pasteurellosis in Rabbits
Pasteurellosis affects multiple body systems in infected rabbits. Breathing signs appear first in most cases. Inner ear infections often develop as secondary problems. Common rabbit diseases include various germ and viral conditions. These affect pet rabbits nationwide.
Clinical exam reveals specific patterns:
- Thick nasal discharge with germ odor
- Swollen lymph nodes under jaw
- Crackling sounds in chest during breathing
- Head tilt showing ear involvement
- Dropped appetite and weight loss
- Tiredness and reduced grooming behavior
Diagnostic Protocol Steps:
- Physical Exam – Complete breathing and systemic assessment
- Lab Testing – CBC, bacterial culture, sensitivity testing
- Imaging Studies – Chest X-rays if pneumonia suspected
- Response Monitoring – Daily assessment of treatment success
Lab tests confirm germ ID and drug sensitivity. Blood work checks for systemic infection spread. X-rays show lung involvement and abscess formation.
Risk Factors for Snuffles in Rabbits
Several factors increase respiratory disease/snuffles risk in pet rabbits. Stress weakens immune systems a lot. Poor air flow allows germs to multiply fast. Overcrowding spreads infections between rabbits quickly.
Major risk factors include:
- Young age (under 6 months) or senior status
- Recent diet changes or travel stress
- Contact with sick rabbits or new pets
- Dusty bedding or poor air quality
- Sudden temperature changes
- Poor nutrition or vitamin lacks
Pregnant rabbits face higher risks. This is due to immune suppression. Male rabbits show slightly higher infection rates than females. Indoor rabbits have lower exposure risks than outdoor pets.
How to Prevent Snuffles in Rabbits
Prevention strategies work better than treatment for breathing infections. Good care practices cut infection risks a lot. Regular vet checkups catch problems early. Treatment works best at this stage.
Key prevention steps:
- Keep clean, dry living space
- Give good air flow without drafts
- Feed high-quality diet with fresh vegetables
- Cut stress through routine schedules
- Quarantine new rabbits for 30 days minimum
- Schedule annual vet exams
- Watch for early warning signs daily
Environment factors play huge roles in prevention success. Keep humidity levels between 40-60%. This is best for breathing health. Remove dusty bedding materials that irritate airways. Finding qualified rabbit vets helps establish preventive care relationships. Do this before emergencies occur.
Find emergency rabbit vet nowVaccination protocols vary by location and risk factors. Some areas recommend Pasteurella vaccines for high-risk rabbits. Discuss vaccination options with rabbit-experienced vets in your area.
Danger Zone: Emergency Warning Signs
Certain signs need immediate emergency vet care. These “red flag” signs show life-threatening problems. They develop fast. Never wait or attempt home treatment when these signs appear.
Emergency Response Checklist (Print and Keep Handy):
□ Breathing rate over 100 per minute
□ Blue or white gums instead of pink
□ Complete loss of appetite for 12+ hours
□ Unable to sit upright normally
□ Body temperature under 100°F or over 105°F
□ Thick discharge blocking nostrils
□ Seizures or loss of consciousness
Call emergency vet services right away when any danger signs appear. Transport rabbits in quiet, warm carriers during crisis situations. Cover carrier with towel to cut visual stress during transport.
Treatment Tables and Protocols
Table 1: Drug Success Against Common Breathing Germs
| Drug | Pasteurella | Staph | Bordetella | FDA Approval | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enrofloxacin | Excellent | Good | Excellent | Yes | 10-28 days |
| Azithromycin | Good | Excellent | Good | Yes | 5-10 days |
| Trimethoprim-Sulfa | Good | Fair | Good | Yes | 14-21 days |
| Chloramphenicol | Excellent | Good | Fair | Limited Use | 10-14 days |
Table 2: Home Care Protocol Safety Comparison
| Treatment Method | Safety Level | Skill Needed | Cost | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medicine Giving | High | Medium | Low | High |
| Steam Therapy | Medium | Low | Very Low | Medium |
| Mist Treatment | High | High | Medium | High |
| Nutrition Support | High | Low | Low | Medium |
| Environment Control | High | Low | Low | High |
Rabbit Respiratory Infection: Dosage Charts
Enrofloxacin (Baytril) Dosing Guide
- Weight: 2-3 lbs → Dose: 0.15-0.25 ml twice daily
- Weight: 3-4 lbs → Dose: 0.25-0.35 ml twice daily
- Weight: 4-5 lbs → Dose: 0.35-0.45 ml twice daily
- Weight: 5-6 lbs → Dose: 0.45-0.55 ml twice daily
Steam Therapy Schedule
- Morning: 5 minutes after breakfast
- Evening: 5 minutes before dinner
- Frequency: Daily for 7-14 days
- Temperature: Warm but not hot
- Supervision: Never leave rabbit alone
This guide gives American rabbit owners evidence-based information. It helps manage breathing infections safely and well. Remember that professional vet care remains key for right diagnosis. It ensures treatment success too. Early help saves lives. It cuts long-term problems a lot.
Find Professional rabbit vet nowStay ahead in rabbit care—subscribe to the Rabbitip newsletter for expert tips, alerts, and bunny-loving advice!
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
How do you treat a breathing infection in a rabbit at home?
Home treatment supports vet care. It cannot replace professional medical help though. Give steam therapy twice daily using bathroom humidity. Keep clean, dust-free environment with good air flow. Offer unlimited fresh hay and quality pellets. This supports immune function. Monitor breathing rate and appetite closely. Contact vet right away if signs worsen. Call if breathing becomes labored too.
Can rabbits survive breathing infections?
Yes, rabbits can survive breathing infections with prompt, right treatment. Success rates reach 85-95%. This happens when drugs start within 48 hours of sign onset. Early help prevents problems. These include pneumonia or inner ear infections. Untreated cases have much lower survival rates. They often lead to chronic illness or death. Age, overall health, and germ strain affect individual outcomes a lot.
Can rabbit snuffles go away on its own?
Germ breathing infections rarely resolve without drug treatment. Mild cases might temporarily improve. But germs remain in the system. Signs return worse than before. Digestive issues often develop as problems from untreated breathing infections. Self-limiting viral infections exist. They are less common than germ snuffles though. Always seek vet diagnosis to determine right treatment needs.
What drugs are used for upper breathing infection in rabbits?
Enrofloxacin (Baytril) serves as the first-choice drug. This works for most rabbit breathing infections. Azithromycin works well for resistant germs. Use it when enrofloxacin causes side effects too. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole treats mixed germ infections well. Chloramphenicol is reserved for severe cases. This is due to potential side effects. Vets choose drugs based on culture results when possible.
How to treat snuffles in rabbits at home?
Home care supports vet treatment. It never replaces professional medical help though. Give prescribed drugs exactly as directed by your vet. Create humidity using bathroom steam therapy. Do 5-minute sessions twice daily. Keep clean, warm environment free from drafts and dust. Offer unlimited timothy hay and fresh water all the time. Proper bunny care includes monitoring breathing rate, appetite, and activity levels daily. Contact your vet if signs worsen. Call if new problems develop too.